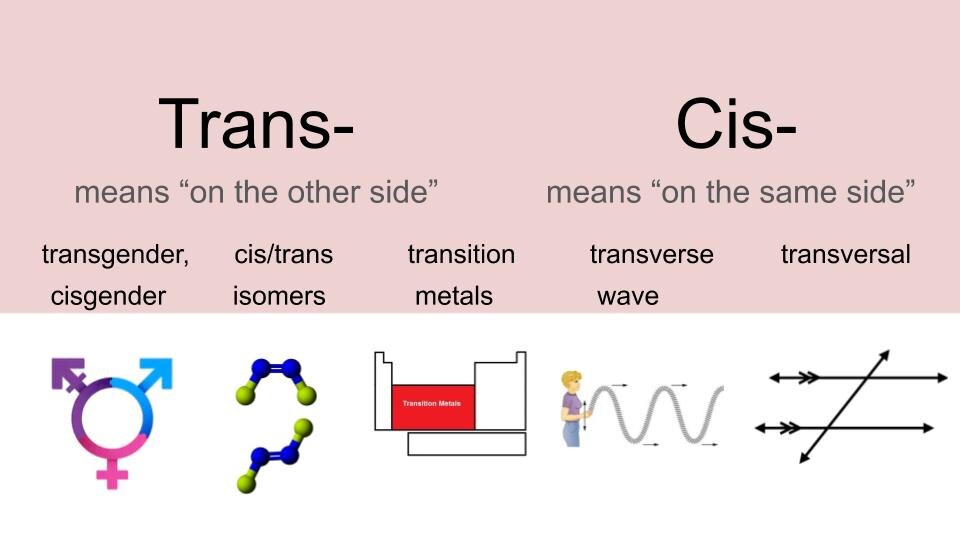
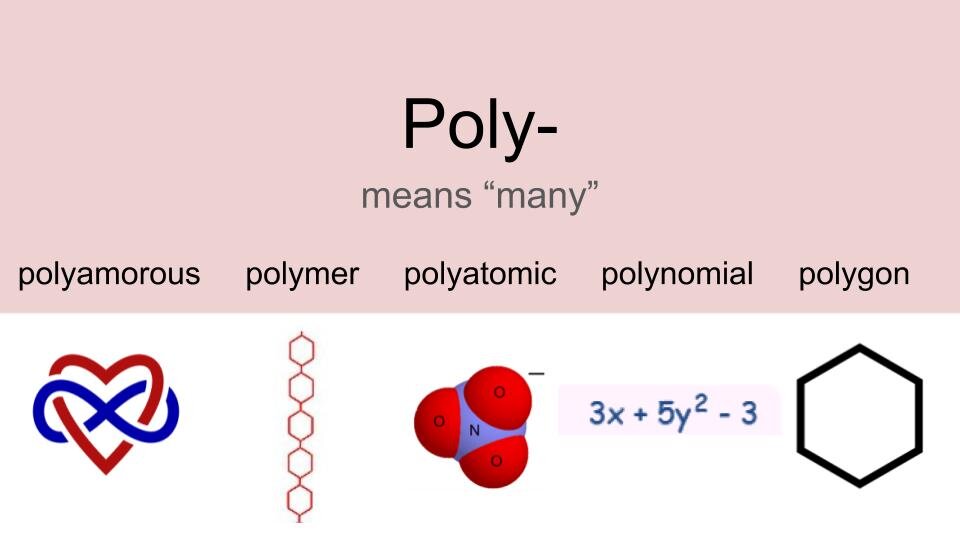
clear infographics (see above for examples),
a checklist with advice for challenging situations such as:
and a statements-editing activity from a workshop by SextEd (a free and confidential texting helpline that answers questions about sex, dating, and health within 24 hours) and ACCM (AIDS Community Care Montreal).
“We also know it can be challenging to use inclusive language when students, peers, or service users don’t, or they’re not familiar with the practice. In these cases, you can still take the time to gently explain why you speak or write the way that you do: to respect the diversity in people’s sexualities, genders, and bodies. If someone asks why you phrased something a certain way, you can take the time to explain why.
In situations where a person is asking a question or speaking in a way that isn’t inclusive, you can....
— Use phrases like “Yes, men, or anyone with a penis, can get an erection at random.”
— Gently remind them of identities they didn’t include in their statement or question, “Yeah, for sure. But I also
think it’s important to keep in mind that some men don’t have penises, and some women do, to make sure we’re
being inclusive.””